Proxmox is a Linux virtualization distribution based on two different hypervisor technologies. KVM is used to offer hardware virtualization and OpenVZ (prior to version 4) or LXC for Linux container virtualization.
Proxmox is a Linux virtualization distribution based on two different hypervisor technologies. KVM is used to offer hardware virtualization and OpenVZ (prior to version 4) or LXC for Linux container virtualization.
Proxmox is based on the latest Debian Linux distribution and still uses the main Debian public repositories to keep the operating system components up to date.
Proxmox can be clustered to span multiple server nodes to provide highly available virtual machines. Combined with Ceph or Gluster, Proxmox is a scalable virtualization platform.
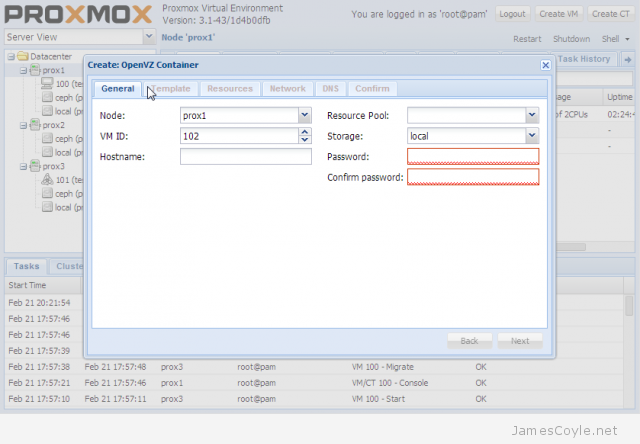
The web based GUI is used to administer Proxmox and give the admin the ability to create new virtual machines and manage storage. The below screenshot is an example of creating an OpenVZ container with the Proxmox web GUI.
Installing Proxmox
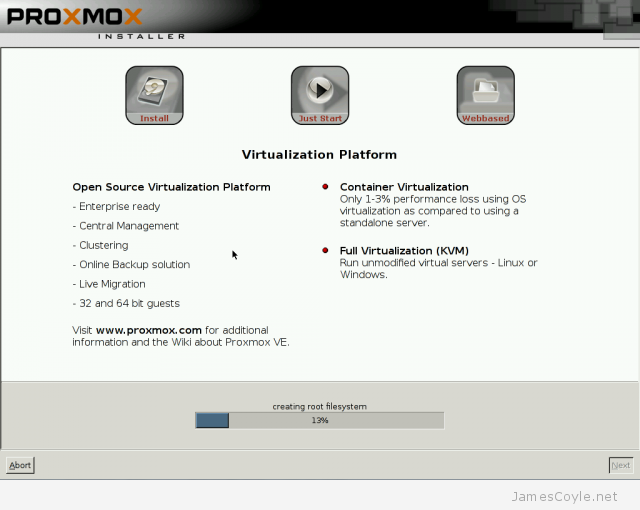
Proxmox is very easy to install – the installer GUI takes care of everything, such as installing the correct packages and partitioning the root hard disk.
You can download Proxmox from the Proxmox download page as an ISO which you will need to boot your server from.
See my Install guide blog post for the basics on installing Proxmox.
Proxmox Poll
Keeping up to date
Updates to Proxmox are delivered via apt-get which is the utility which manages packages on Debian. When new updates are available you simply run the below commands to update your system.
Note: you will need to shutdown all running VMs and OpenVZ containers before running the update.
Run apt-get update to download the information on the latest available updates.
apt-get update
Run apt-get dist-upgrade to download and install the latest updates.
apt-get dist-upgrade
Further reading
See the Proxmox tag for more information on Proxmox.